A Short SEO Dictionary
A lot of people probably struggle with SEO terminology, and understandably so. We throw around a lot of terms and sometimes I’m even guilty of interchanging words that means different things – or even making up my own terms.
Therefore, I’ve compiled 10 terms for those of our readers who want to know how to communicate about their search engine optimization strategy, statistics, etc.
Backlink – A link from an external website to your own website. In the past, these could be artificially, automatically or otherwise “illegitimately” obtained in order to trick Google into thinking that your website was hot stuff. Now, Google has developed measures to penalize websites that contain “low-quality” backlinks, and certainly sites with tens, hundreds or thousands of these links, which often come through schemes and the like.
Content – Anything that appears directly on your website or in your social media outlets, including words, images, videos and more. The best medicine for any site is to have high-quality, helpful content directly on site. However, offsite content on social networks can create engagement and provide more avenues for people to find your site.
Internal Link – These are links within your site to other pages within your site. This can include navigation linking, links within content, or even links in images. For users, links offer a helpful way to navigate a site and find helpful information. For search engines, they index this information and it can act as a “map” to see which words and pages are important to your business.
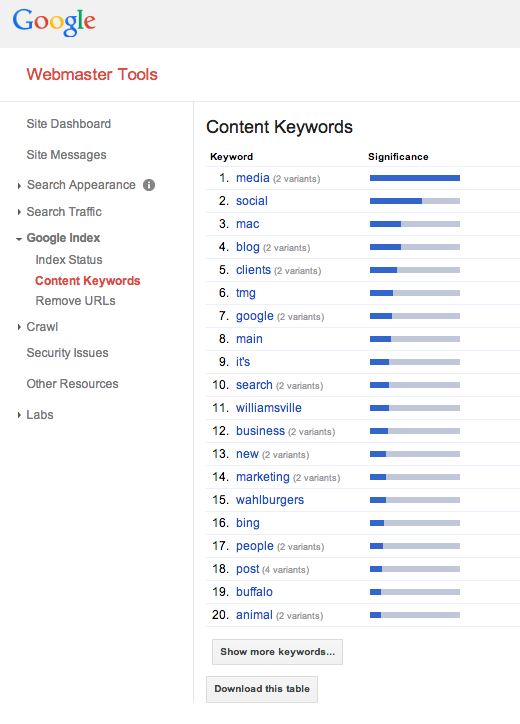
Keyword – Technically, a keyword is any single word that appears on your site. Words that appear more throughout your site in a natural way end up being targeted as information that search engines can see as important. Keywords often get confused with queries and phrases, which typically contain a strong of words, as opposed to single words.
Meta – Meta tags, in search engine optimization, include “background” information that stresses important keywords for search engines, including the “title,” “description,” and “keyword” tags – the latter of which is not longer factored into Googles ranking algorithm. These bits of data do not appear on your webpage, but will appear in a search engine’s result for the page.
Organic – This refers to search results that are not paid for. When you search on Google, you will often see “ads,” for which companies pay to rank. Organic results, however, are based on actual website content, in order to direct people to results that actually give them what they wanted to find. Technically, a dentist website in Portland could easily pay to rank for the query “coffee shops in Buffalo” and land a top spot in the Google ads. However, they would not be able to rank organically without changing most, if not all of their website into a coffee shop site, based in Buffalo.
Query – A query is a phrase that a user types into a search engine in order to find a relevant website. Typically, a query contains several keywords, making it a phrase as opposed to a singular keyword. In SEO, one of the best ways to achieve success is to research and deduce queries that users actually type on a monthly basis. Then, you incorporate these phrases into your site content, meta tags and social media in order to stress your website’s relevance insofar as those specific queries are concerned.
Ranking – A numerical ranking refers to the placement of your website in a search engine result for a particular query. 1-10 appear on the first page, 11-20 on the second and so on. It is important to remember that rankings fluctuate from computer to computer, location to location and time to time. Furthermore, Google does not index your site and assign you a number. Rather, they apply their algorithms to the info on your site and when a user enters a query, the algorithm dictates you placement based on both the information on your website and the information particular to the user.
SEO – Search engine optimization refers to the process of preparing a website to perform better in a search engine for queries particular to the website’s industry, geography and specializations. The process by which this is done changes when search engines, particularly Google, change or update their algorithms to stress different factors of a website’s “quality.” Furthermore, competition comes into play, as other websites with similar desired outcomes may or may not also employ correct tactics in their fight for top placement.
SERP – Search engine results pages appear when a user enters a query in a search engine. These include organic results, paid ads, map information, images, etc.
—–
Find me on Google
Tags: Buffalo NY SEO, Google